[ad_1]
The hurdles appear fairly difficult.
We simply launched a report that explores the chances and limitations of A number of Employer Plans (MEPs) to enhance protection in employer-sponsored retirement plans. The shortage of constant protection – a urgent concern for the nation’s retirement earnings safety – is pushed by small employers.
A MEP is a retirement plan – typically a 401(ok) – adopted by two or extra employers and administered by a MEP sponsor (sometimes a commerce or business group or skilled employment group) that takes on the fiduciary burden and spreads the executive, compliance, and value burden throughout a number of employers.
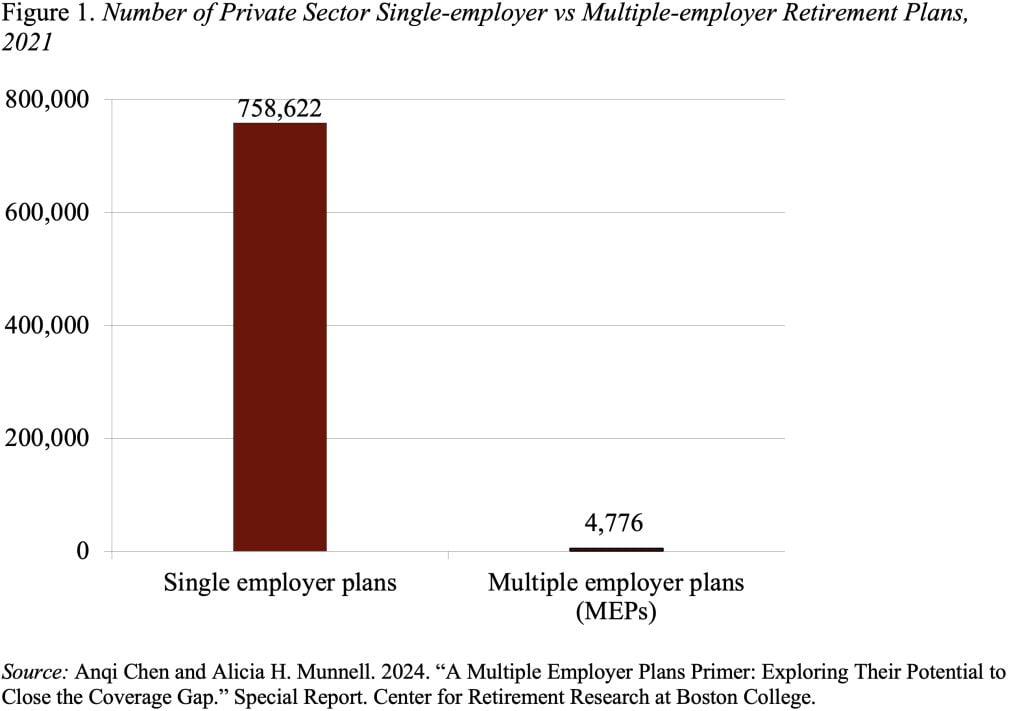
Whereas MEPs have been round for many years, they haven’t moved the needle on protection. In 2021, MEPs solely represented 0.6 % of whole private-sector retirement plans (see Determine 1), overlaying roughly 5.7 % of lively contributors. Two principal restrictions of MEPs could have restricted their adoption: 1) employers needed to share a typical bond; and a couple of) the entire MEP might lose its tax-qualified standing if one employer throughout the group was not in compliance (the “dangerous apple” rule).
To extend participation, The SECURE Act of 2019 eliminated the “dangerous apple” restriction and created a brand new subclass of MEPs, referred to as Pooled Employer Plans (PEPs), which aren’t restricted to employers with a typical bond. PEPs can solely be established by a registered pooled plan supplier (PPP), which takes on the function of named fiduciary and attends to plan administration, compliance, and auditing.
The elimination of the frequent bond and dangerous apple restrictions has generated a number of pleasure, notably amongst monetary companies corporations. Certainly, PEPs have a number of potential benefits over the plethora of present choices for small employers. PEPs can cut back the executive burden, the fiduciary accountability and – maybe – the price of providing a plan, whereas sustaining the flexibility to pick the supplier of alternative and provide employer matches.
Regardless of the keenness, the preliminary uptake has been sluggish and PEPs could have a restricted impression on the protection hole for a lot of causes.
- Overwhelming majority of small employers have by no means heard of PEPs or their guardian, MEPs. Suppliers is not going to solely should persuade employers that providing a retirement plan is efficacious, however that becoming a member of a PEP is the suitable choice for them.
- Price financial savings could not materialize. First, it might be onerous to beat the price of offering a single employer plan, which has declined dramatically. Second, elevated competitors within the MEPs market might promote decrease charges, however employers with weak bonds might additionally pay much less consideration to plan prices. Lastly, plans which might be free (or nearly free) to the employers invariably go on prices to plan contributors.
- Employer retains some fiduciary duties. Whereas the PPP is the named fiduciary for a PEP, the employer is accountable for choosing the suitable supplier, monitoring the charges, and figuring out whether or not the companies provided are useful.
- Exiting could also be tough. An employer that will get greater and desires to transform to a extra customizable single-employer 401(ok) could discover it tough and time-consuming to terminate its portion of the PEP.
- PEPs may make mergers and acquisitions more difficult. Whether or not an employer needs to merge its plan with a purchaser’s plan or fold an acquired employer’s plan into its personal plan, the method is far simpler with a single-employer plan.
- Future development in PEPs could not imply larger protection. It might merely imply employers are opting to affix a PEP reasonably than provide their very own single-employer plan.
Clearly widespread adoption of PEPs faces a number of hurdles; solely time will inform whether or not this much less restrictive model of MEPs makes a dent in protection.
[ad_2]

